Ensure resiliency and optimized resource consumption with load balancer & circuit breaker
When the number of users increase to the point that one region or server where the application have trouble responding to requests in a reasonable time. This creates a user experience where the app feels slow. To avoid this poor user experience, load balancing can be used. With "load balancing" you set up multiple endpoints capable of serving requests and additionaly configure a scheme for how the "balancing" should happen.
Scenario: The Challenge of LLM Resiliency
When building AI applications that rely on Large Language Models (LLMs), ensuring reliable and cost-effective access to these models presents several challenges:
- Service Availability: What happens when an Azure OpenAI service experiences downtime or throttling?
- Regional Reliability: How do you maintain operations if a specific Azure region faces issues?
- Cost Optimization: How can you balance between reserved capacity (Provisioned Throughput Units PTU) and consumption-based pricing?
- Performance: How can you ensure consistent response times for users regardless of backend load?
Without proper management, these issues can lead to application failures, inconsistent user experiences, and unexpected costs. When your primary OpenAI service fails, your application users typically receive error messages until the backend issue resolves - a frustrating experience especially for mission-critical applications.
Video
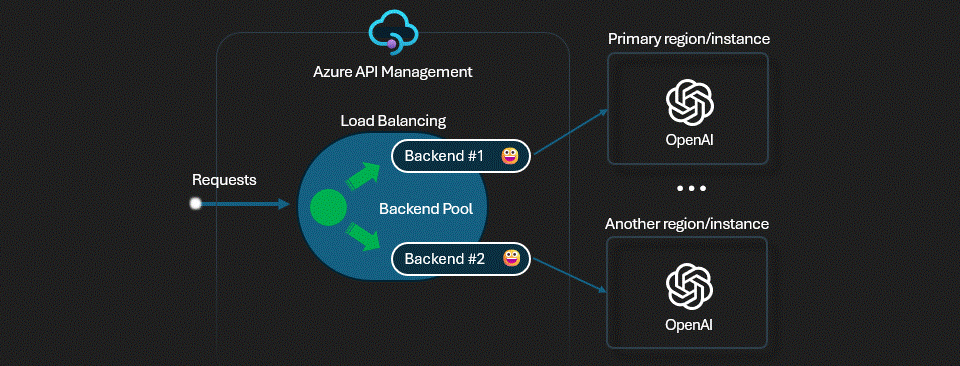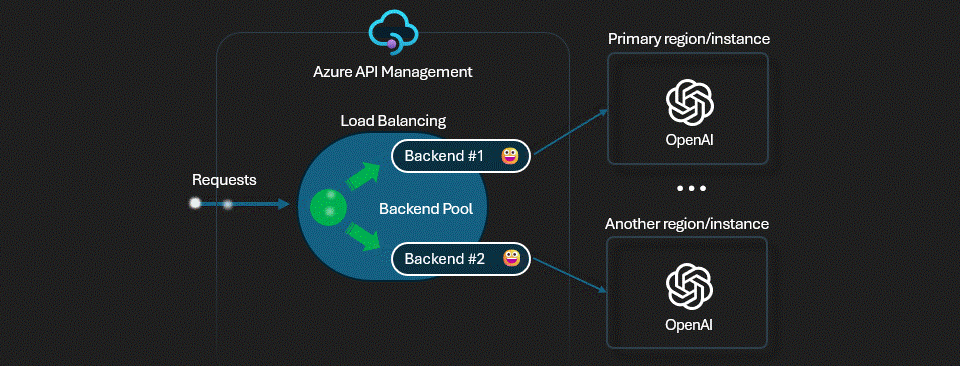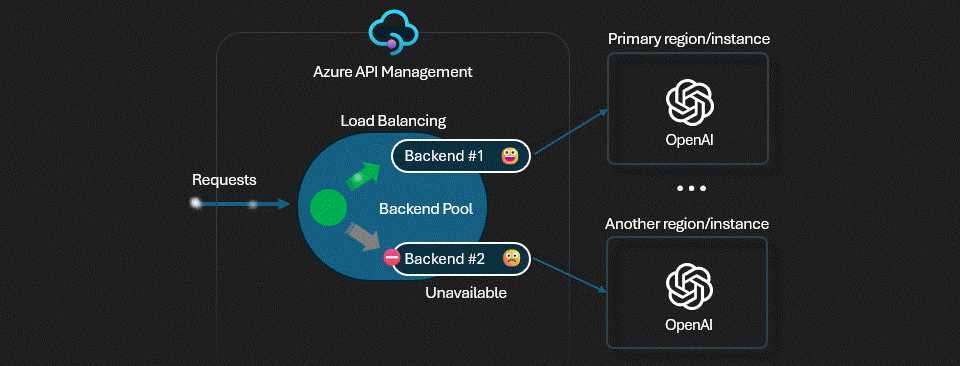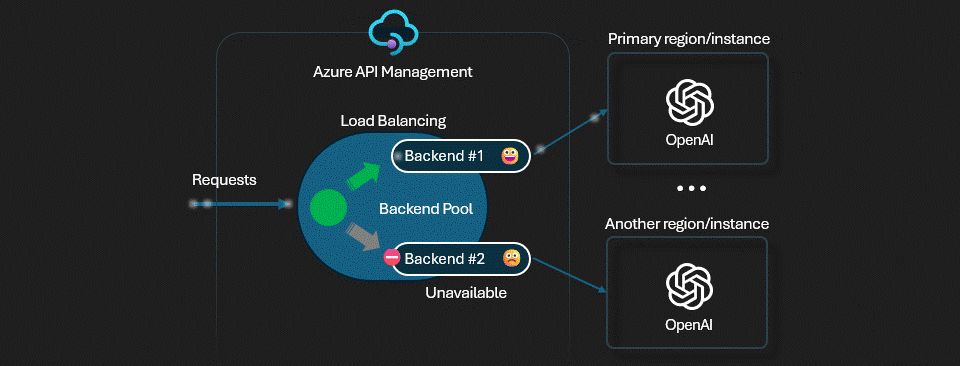
Solution: Backend Pool Load Balancing in Azure API Management
Azure API Management (APIM) provides a powerful solution through its backend pool functionality that allows you to:
- Distribute Load: Route requests across multiple Azure OpenAI services
- Implement Failover: Automatically redirect traffic when primary services are unavailable
- Optimize Resource Usage: Prioritize dedicated capacity before falling back to consumption-based instances
- Manage Traffic Intelligently: Use priority and weight-based routing for fine-grained control
Understanding the Prioritized PTU with Fallback Scenario
The pattern we'll implement is a Prioritized PTU with Fallback Consumption scenario with:
- Primary Tier (Priority 1): A Provisioned Throughput Unit (PTU) Azure OpenAI service that offers dedicated capacity at a fixed cost
- Secondary Tier (Priority 2): Multiple consumption-based Azure OpenAI services that you only pay for when used
This pattern will allow you to:
- Maximize utilization of your pre-paid PTU capacity
- Automatically scale to consumption-based instances when demand exceeds PTU capacity
- Maintain service availability even if one or more regions experience issues
Exercise - Set up load balancing
Make sure you have completed the lesson on setting up cloud resources before continuing.
To make load balancing happen, we need at least two instances of Azure Open AI, an Azure API Management instance and configuration instructing how the "balancing" should happen.
-1- Configure API Management (Backend Pool)
-
First you'll need to get the Endpoint URLs for each of your Azure OpenAI services.
- Navigate to your Azure OpenAI resource and click on Endpoints, then copy the Endpoint and save it for a later step.
- Do this for all three Azure OpenAI services.
-
Navigate to your API Management service and expand the APIs section
-
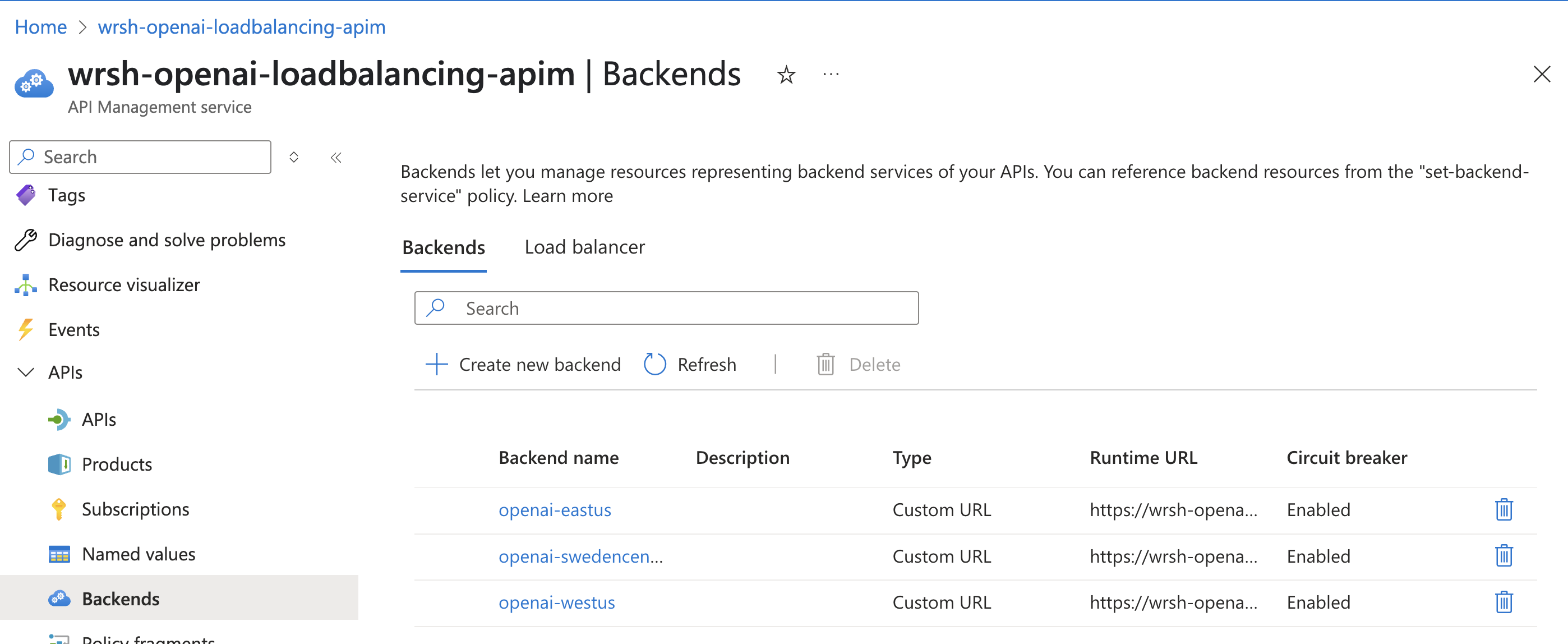
You will now add the Azure OpenAI services as backends to your API Management service. Click on Backends and then + Create new backend
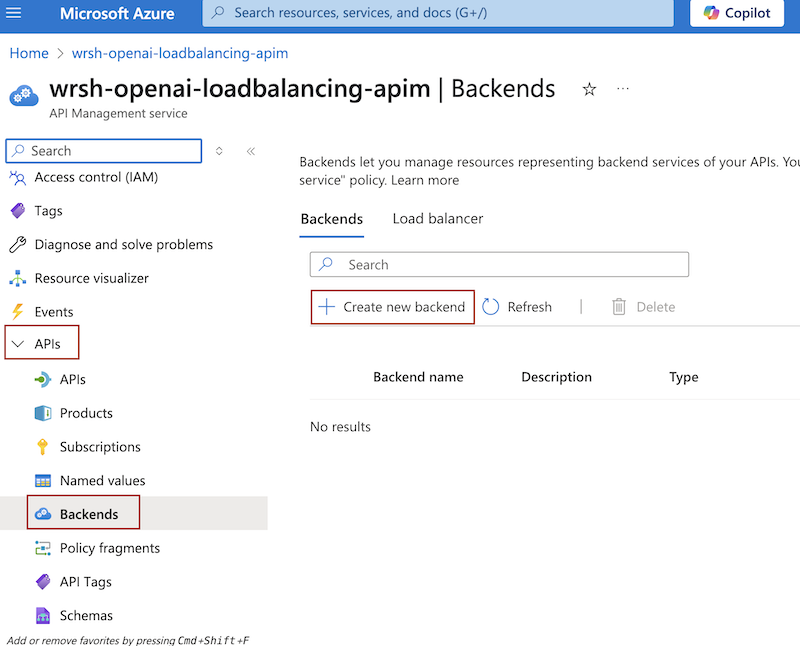
- Enter a Name (e.g.,
openai-eastus) - Select Custom URL as the Backend hosting type
- Paste in the Endpoint URL you copied earlier
Backend pool
Skip this for now, as we will create a load balanced pool in the next step
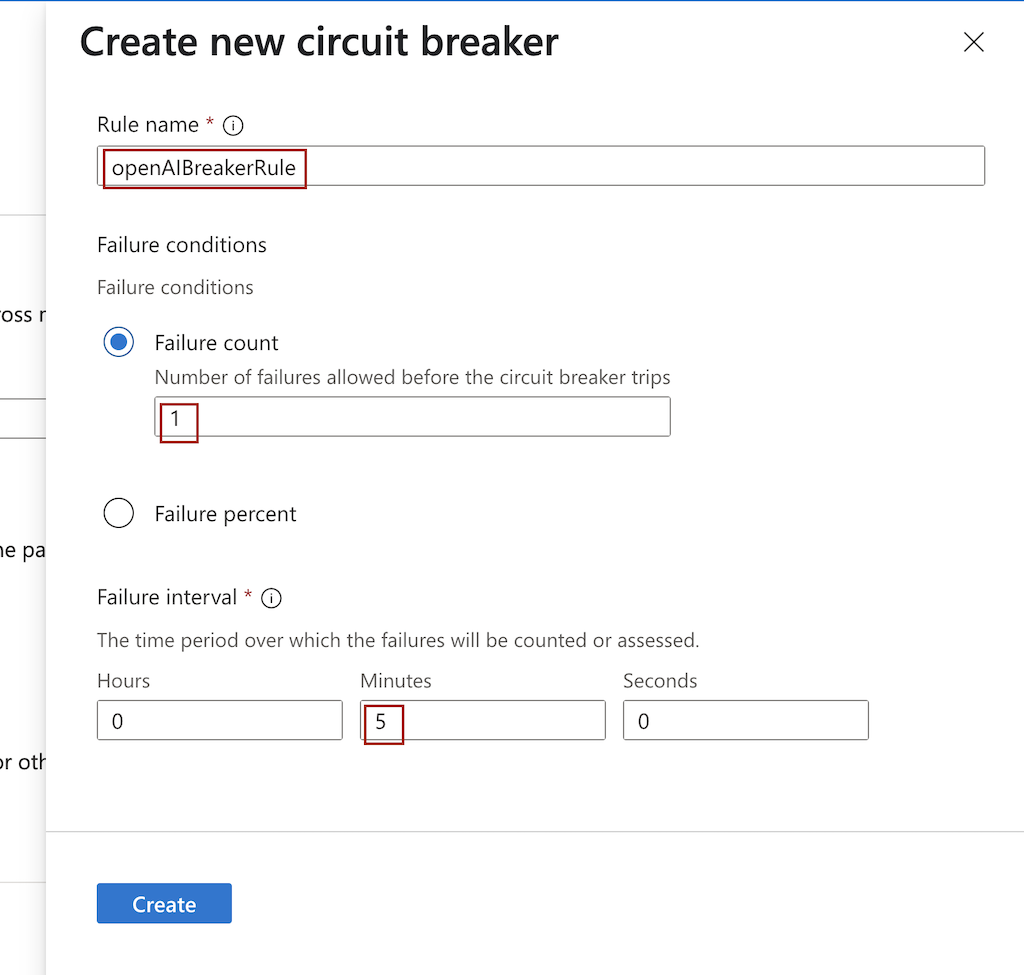
Circuit breaker rule
- Click on + Create new for the Add a circuit breaker rule option
- Enter a Name (e.g.,
openAIBreakerRule) - Leave Failure count as 1
- Set Failure interval to 5 minutes
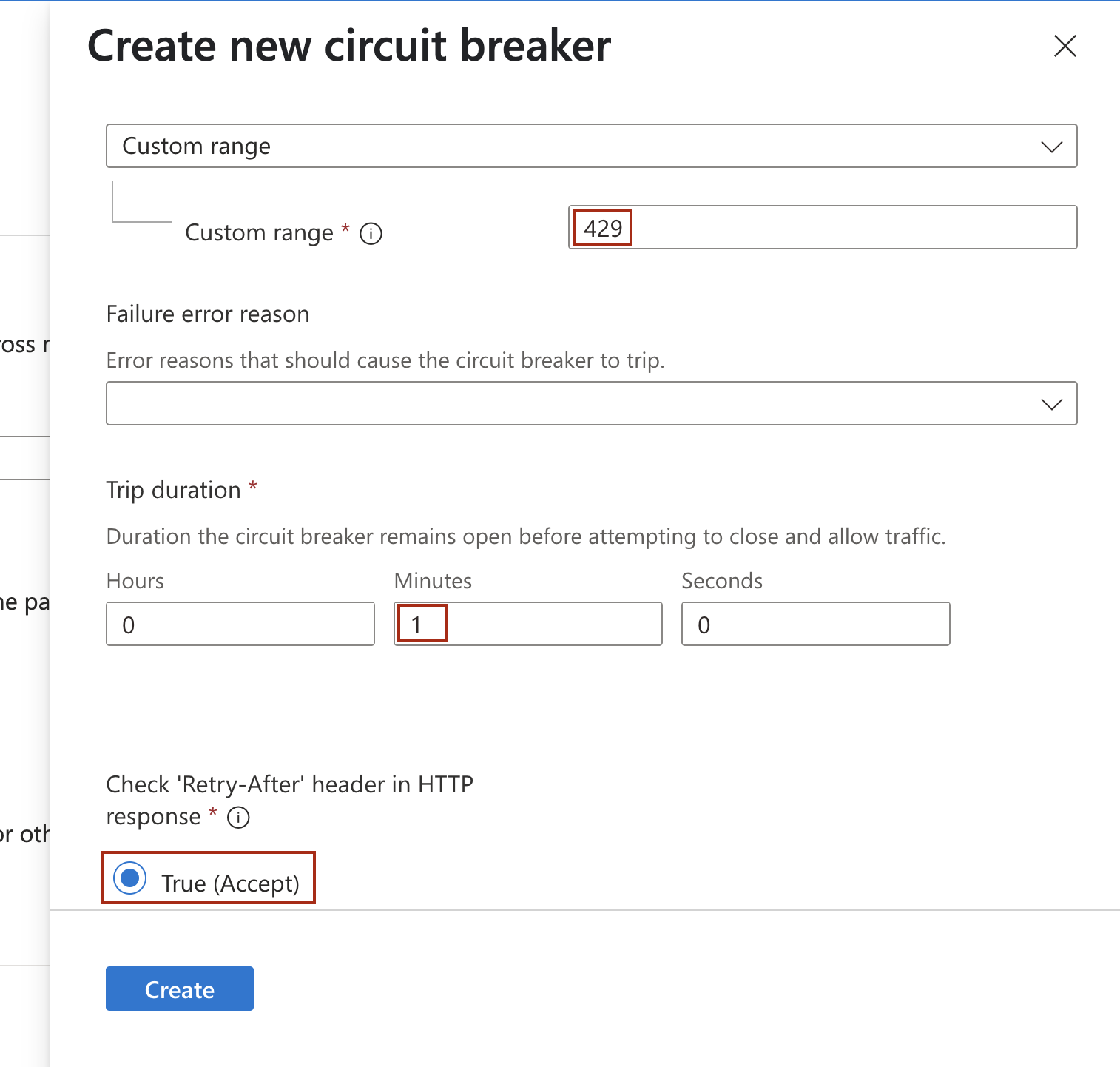
- Specify Custom range as 429
- Set Trip duration to 1 minute
- Check True (Accept) for the Check 'Retry-After' header in HTTP reponse
- Enter a Name (e.g.,
- Enter a Name (e.g.,
-
Click on Create to add the Azure OpenAI service as a backend
-
Repeat the above steps for the other two Azure OpenAI services, ensuring you set the same circuit breaker rule for each backend
-
Backend 2
- Name:
openai-westus - Circuit breaker rule:
openAIBreakerRule
- Name:
-
Backend 3
- Name:
openai-swedencentral - Circuit breaker rule:
openAIBreakerRule
- Name:
-
- Next, you will need to create a Load Balanced Pool for your Azure OpenAI services. Click on Load balancer and then + Create new pool
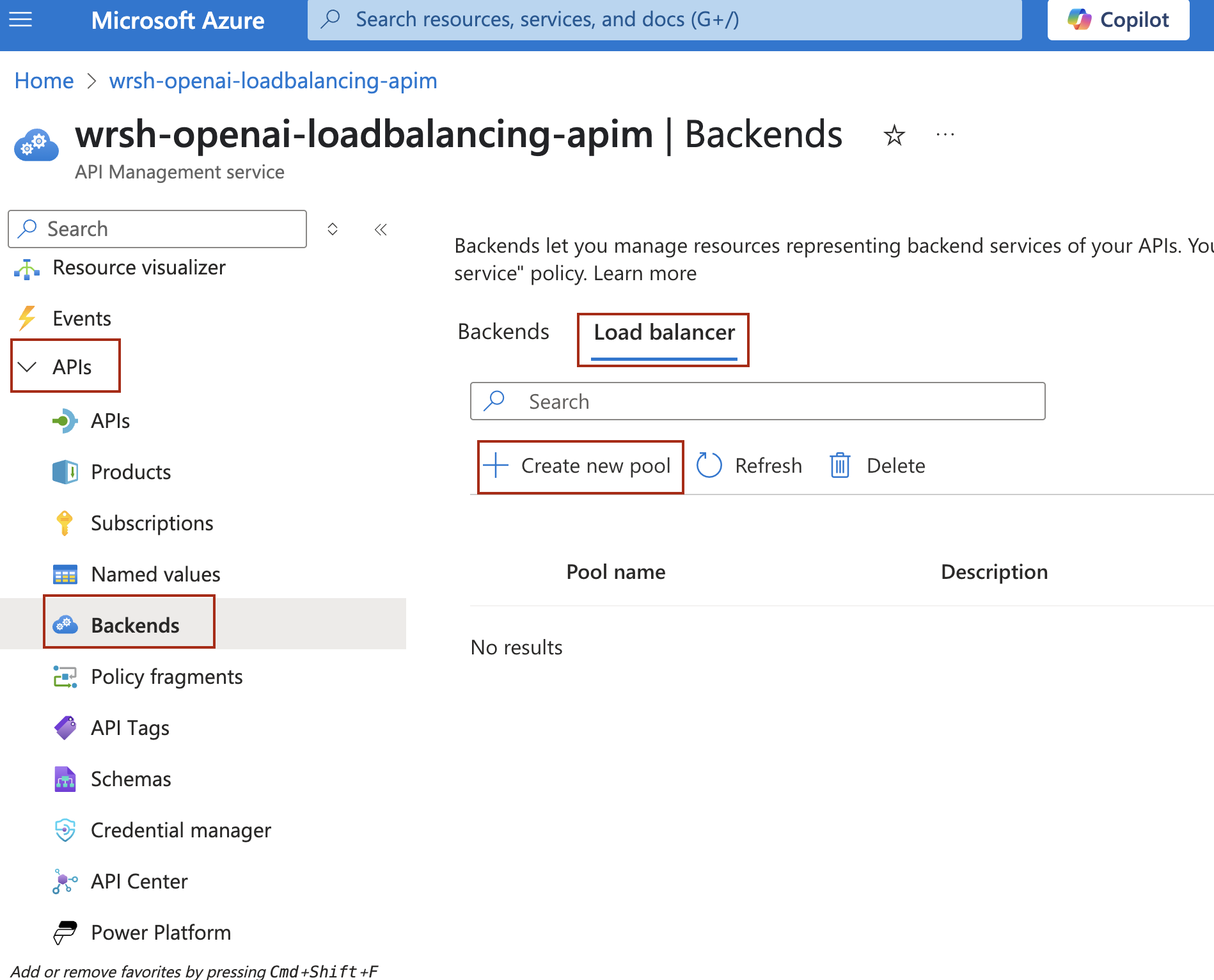
- Enter a Name (e.g.,
openai-backend-pool) - Check all three backends you created earlier for the Add backends to pool option
- Leave the Backend weight and priority as Send requests evenly to distribute requests evenly across all backends (Round Robin)
- Enter a Name (e.g.,
-2- Import Azure Open AI to your Azure API Management instance
-
In your API Management service, click on APIs, scroll to Create from Azure resource and then select Azure OpenAI Service
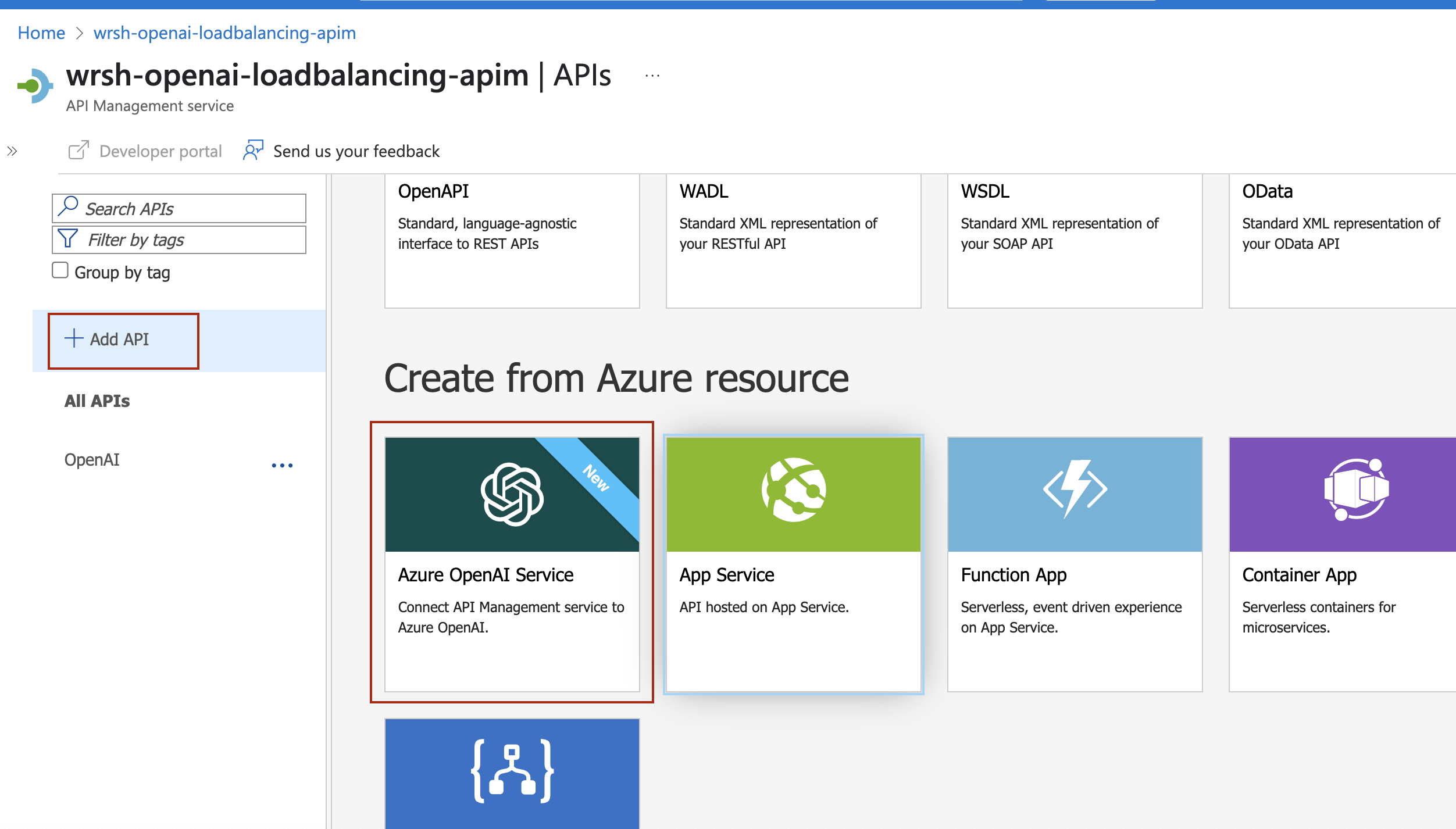
- Select an Azure OpenAI instance (e.g.,
wrsh-openai-eastus) - Select 2024-02-01 as the Azure OpenAI API version
- Enter a Display name (e.g.,
OpenAI) - Check the Improve SDK compatibility option, which will postfix the base url with
/openai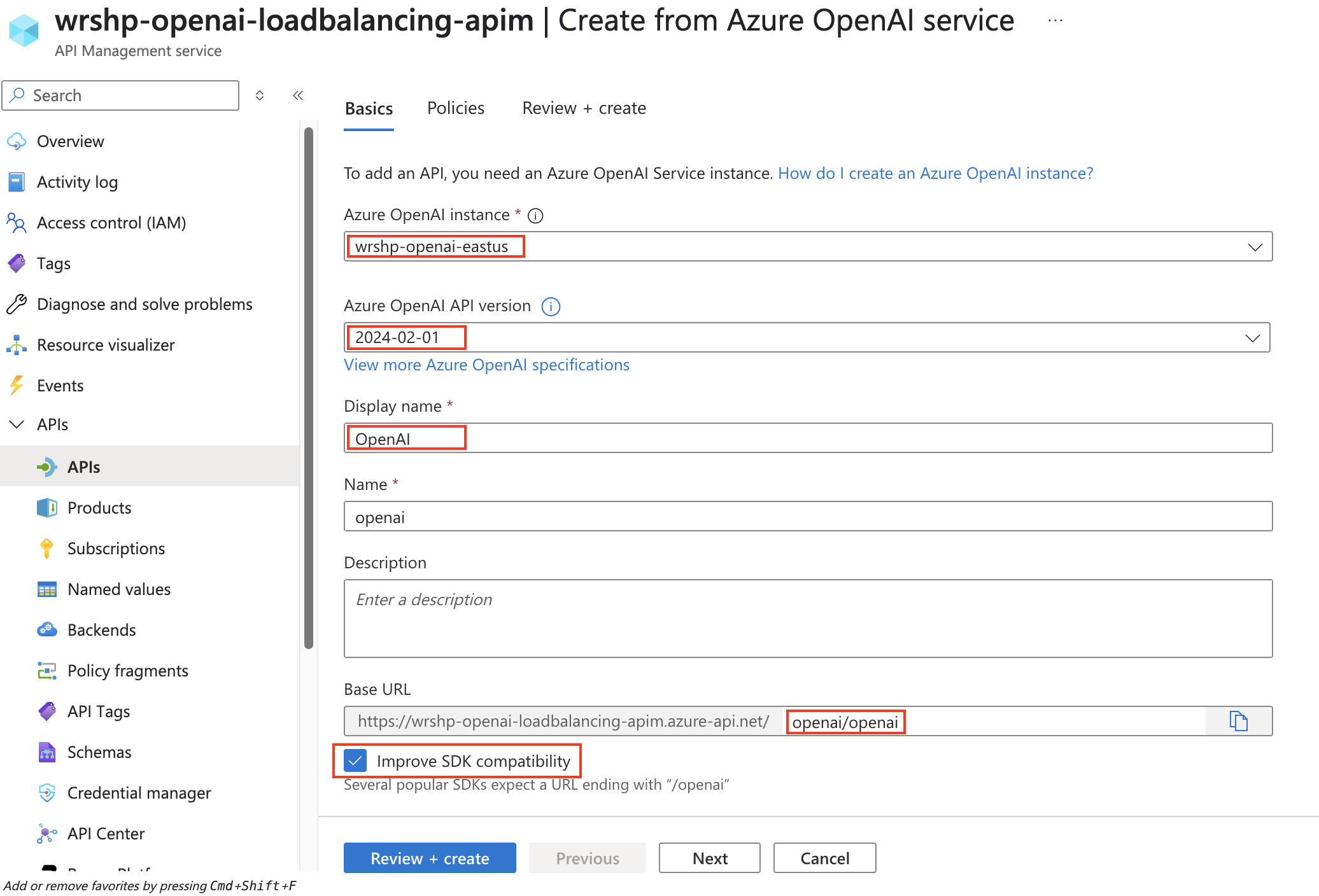
- Click on Review + Create and then Create
- Select an Azure OpenAI instance (e.g.,
-
You now need to configure API Policies for the API you just created. Click on APIs and select the API you just created (e.g.,
OpenAI)-
Select Design, then Inbound processing and click on the "Policy Code Editor" icon to open the policy editor. Replace the existing policy with the following code:
<policies>
<inbound>
<base />
<authentication-managed-identity resource="https://cognitiveservices.azure.com" output-token-variable-name="managed-id-access-token" ignore-error="false" />
<set-header name="Authorization" exists-action="override">
<value>@("Bearer " + (string)context.Variables["managed-id-access-token"])</value>
</set-header>
<set-backend-service backend-id="openai-backend-pool" />
</inbound>
<backend>
<!--Set count to one less than the number of backends in the pool to try all backends until the backend pool is temporarily unavailable.-->
<retry count="2" interval="0" first-fast-retry="true" condition="@(context.Response.StatusCode == 429 || (context.Response.StatusCode == 503 && !context.Response.StatusReason.Contains("Backend pool") && !context.Response.StatusReason.Contains("is temporarily unavailable")))">
<forward-request buffer-request-body="true" />
</retry>
</backend>
<outbound>
<base />
</outbound>
<on-error>
<base />
<choose>
<!--Return a generic error that does not reveal backend pool details.-->
<when condition="@(context.Response.StatusCode == 503)">
<return-response>
<set-status code="503" reason="Service Unavailable" />
</return-response>
</when>
</choose>
</on-error>
</policies>This policy does the following:
- Uses a managed identity to authenticate with the Azure OpenAI service
- Sets the backend service to the load balanced pool you created earlier
- Implements a retry policy that retries requests to the backend if it receives a 429 (Too Many Requests) status code or a 503 (Service Unavailable) status code
-
Click on Save to save the policy
-
Exercise: Test your Load Balancing Setup
-1- Test round-robin
Round-robin load balancing is the default behavior of Azure API Management. API Management will distribute requests evenly across all backends in the pool. To test this,
-
In your APIM instance, go to "APIs" and select your "OpenAI" API
-
Select the
POST Creates a completion for the chatoperation -
Select Test and for
Template parameters:
- deployment-id:
gpt-4o-mini - api-version:
2024-02-01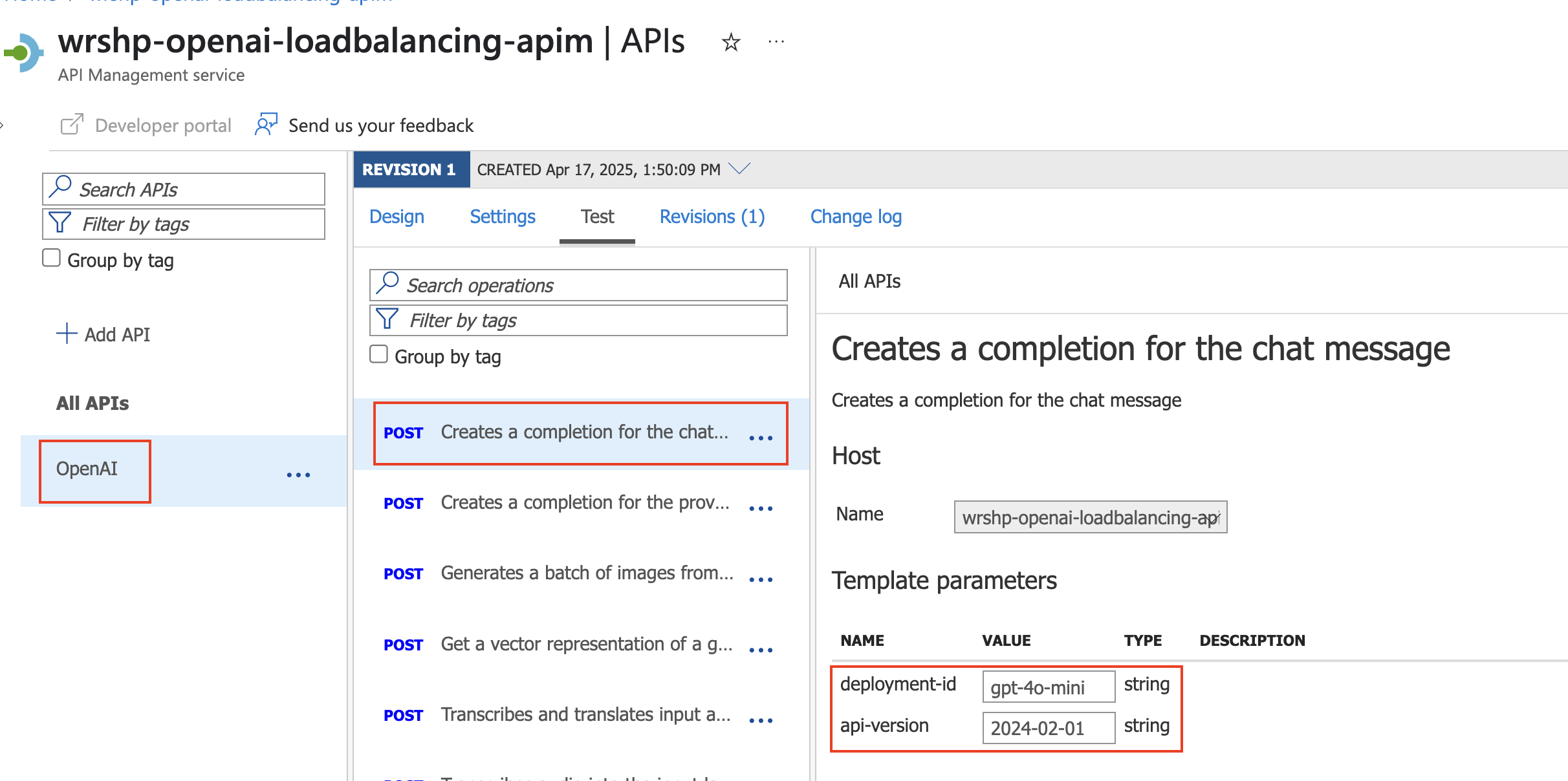
Request body:
{
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a sarcastic, unhelpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the weather like today?"}
]
} - deployment-id:
-
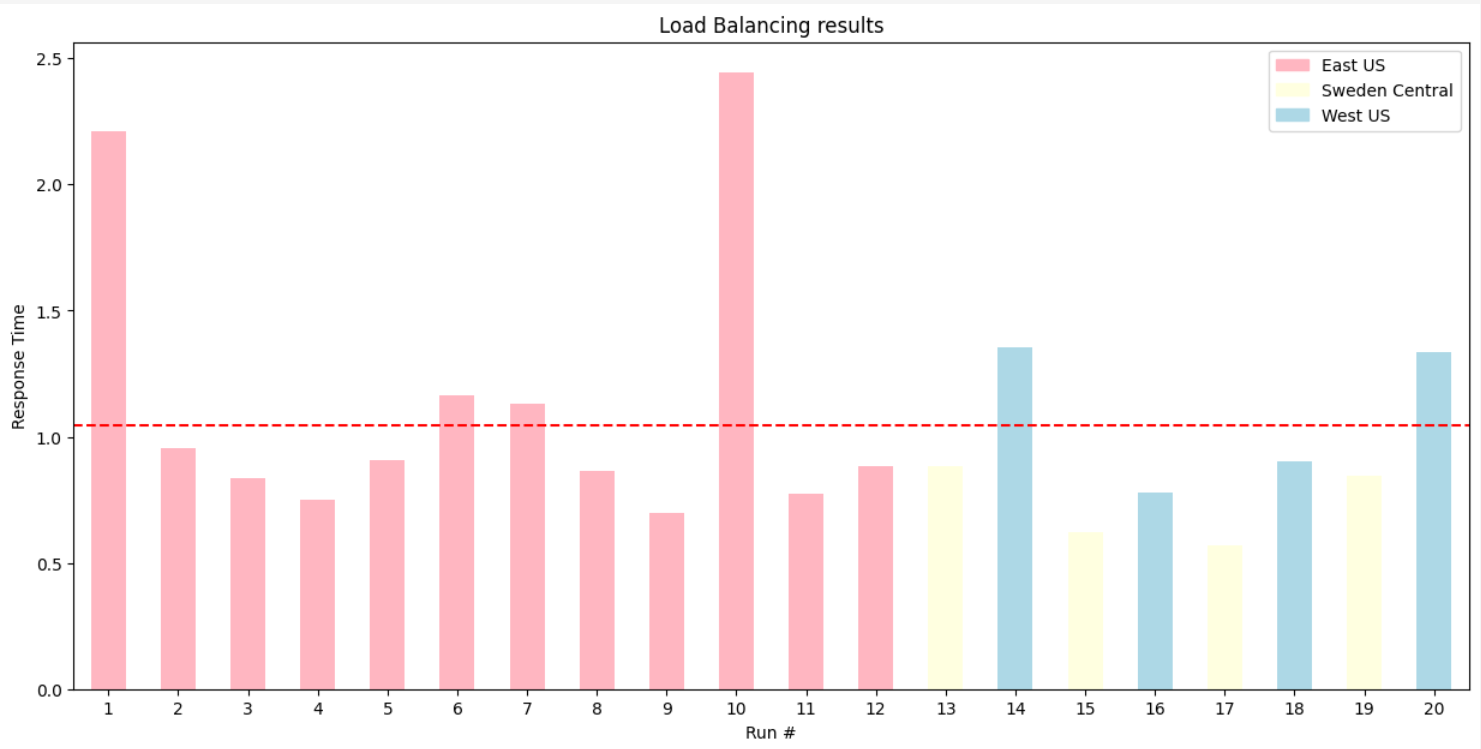
Click on Send to send the request. Run the test multiple times and observe the "x-ms-region" header in the response. You'll notice that the requests are being distributed evenly across all three backends in the pool (East US, West US, and Sweden Central).
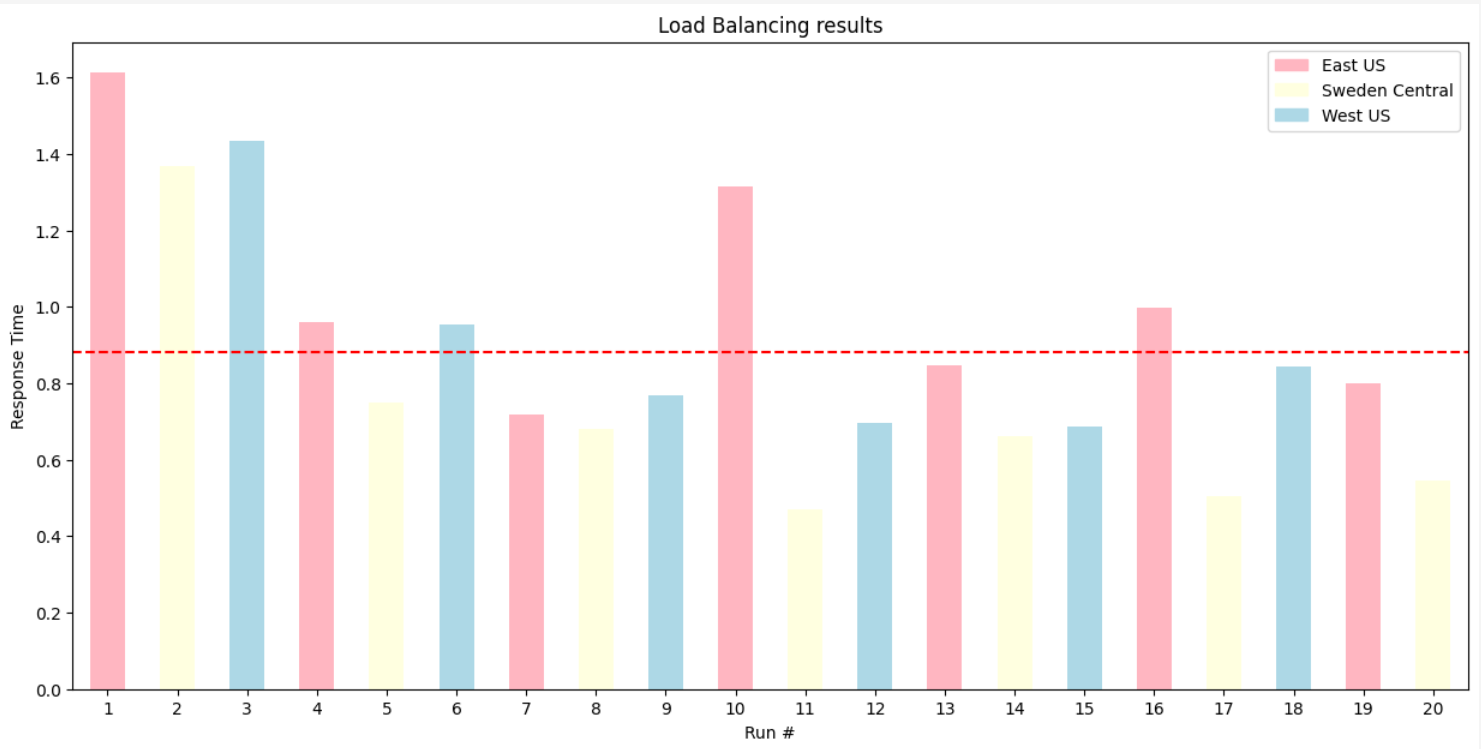
-2- Test Priority-Based Load Balancing
Priority-based routing ensures backends with lower priority values (high priority) get traffic first. Only when higher-priority backends are unavailable or overloaded will traffic flow to lower-priority backends.
Note:
- Higher weight values receive proportionally more traffic
- Used to distribute load between equally important backends
- Can be adjusted to account for different backend capacities
For example, if you were to set the following priorities:
- East US: Priority 1
- West US: Priority 2
- Sweden Central: Priority 3
The expected behavior would be that requests would be sent to the East US backend first. If it is unavailable, requests would then be sent to the West US backend, and finally to the Sweden Central backend.
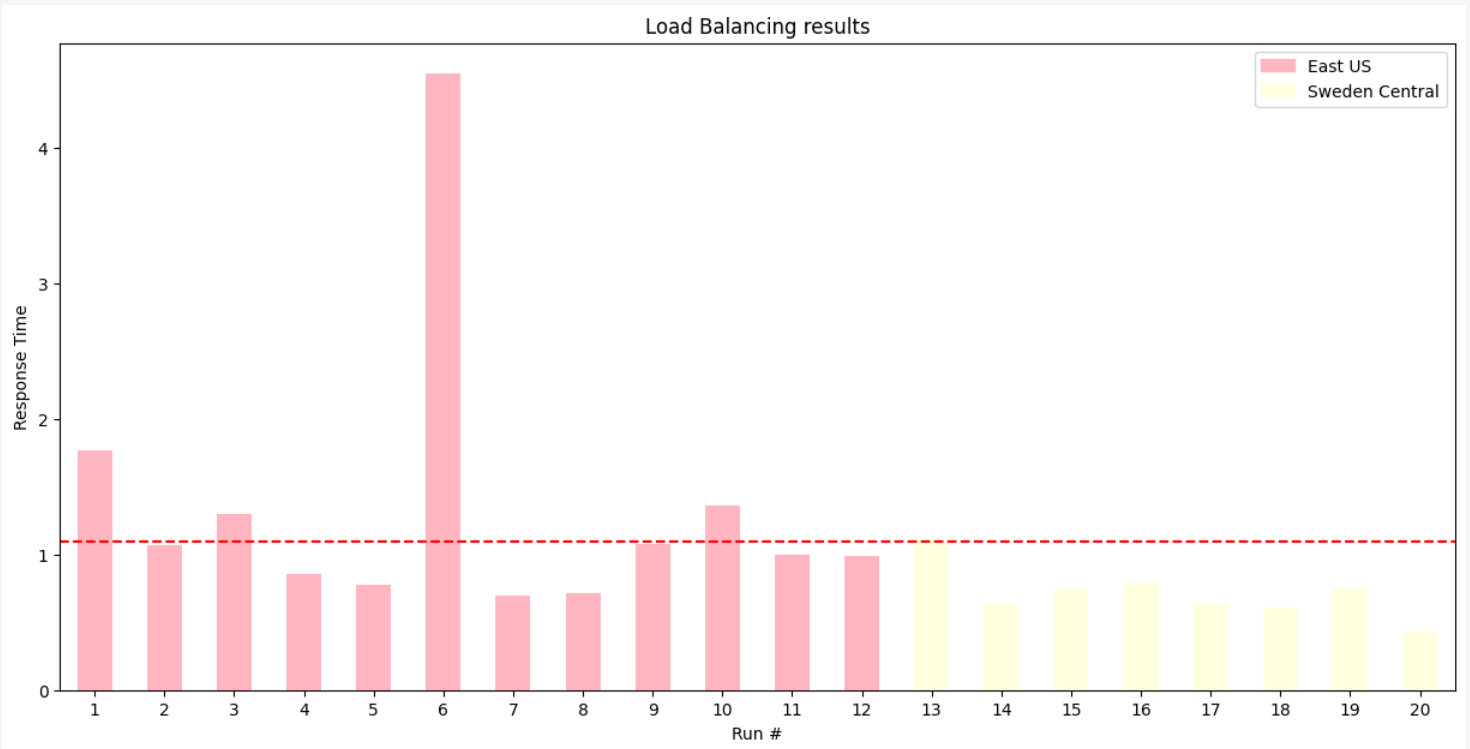
-3- Test Weighted Load Balancing
Weighted load balancing allows you to assign different weights to each backend in the pool. This means that some backends will receive more traffic than others based on their assigned weight. Within the same priority level, weights determine the proportion of traffic each backend receives:
To test this, you will need to update the backend pool configuration to set priorities for each backend:
-
In your APIM instance, go to Backends, switch to Load balancer and select the openai-backend-pool you created earlier
-
Click on Backends and select the Customize weight and priority option, then set the following:
- East US: Priority 1
- West US: Priority 2, Weight 50
- Sweden Central: Priority 2, Weight 50
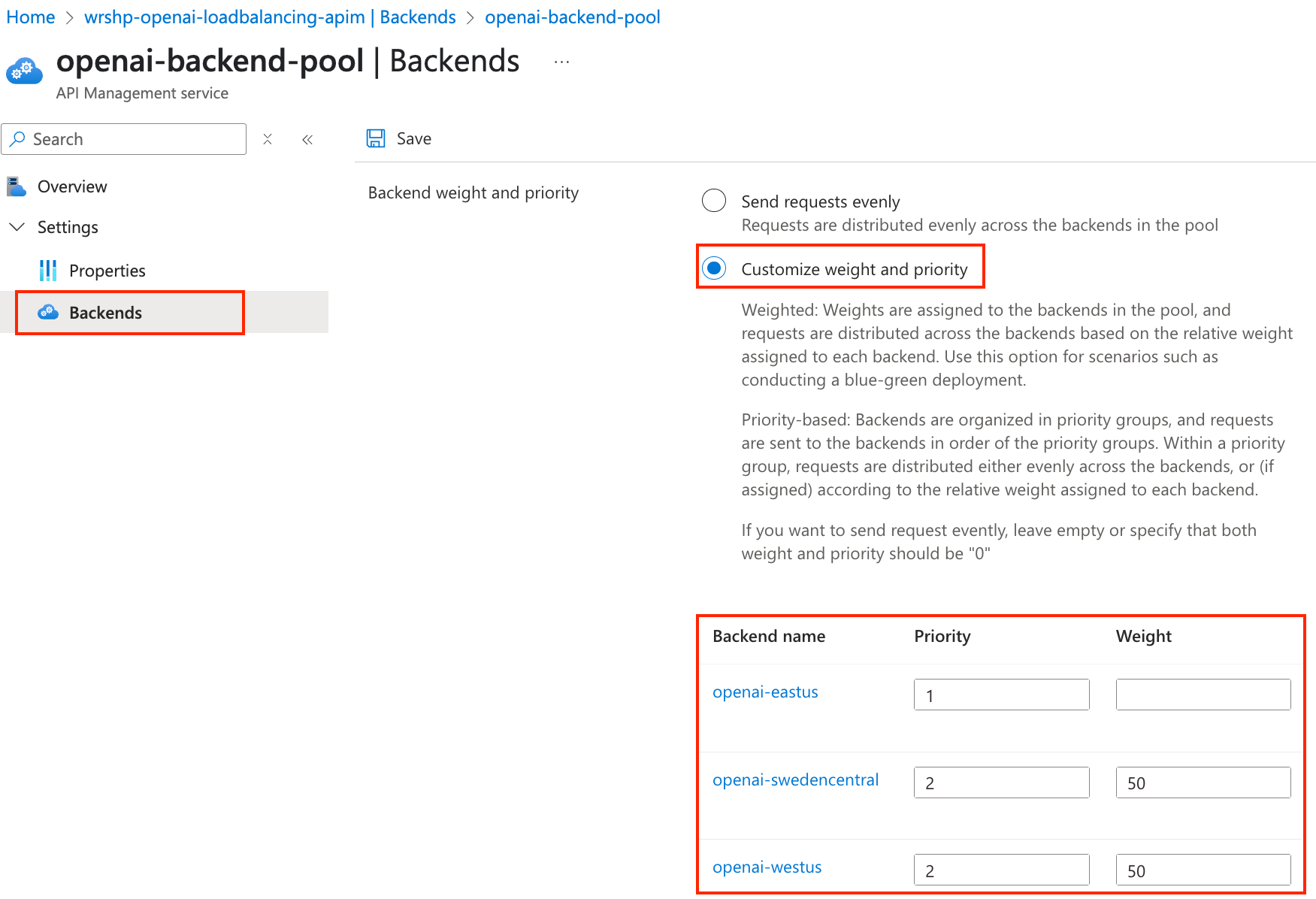
-
Click on Save to save the changes
-
Now return to the APIs section to test the API again. You can use the same test as before, but this time you should see that the requests are being distributed based on the weights you set. The East US backend should receive more traffic than the West US and Sweden Central backends.
Conclusion
You learnt how to set up automated load balancing and failover for your Azure OpenAI services using Azure API Management. This setup allows you to ensure high availability, optimize resource usage, and provide a seamless experience for your users even in the face of backend failures.
Additional Resources
-
Docs: Load balancing
-
Blog post: Improve LLM backend resiliency with load balancer and circuit breaker rules in Azure API Management
Infrastructure as Code
- Lab: load balancing