Test the application through the publicly available endpoint
Now that you have deployed each of the microservices, you will test them out to see if they were deployed correctly. Also inspect wether all pods are properly up and running. In case they are not, inspect the logs to figure out what might be missing.
Step by step guidance
-
You configured both the api-gateway and the admin-server with a loadbalancer. Double check whether public IP’s were created for them.
kubectl get services -n spring-petclinicThis should output info similar to this.
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE admin-server LoadBalancer 10.0.73.174 20.245.56.122 8080:32737/TCP 160m api-gateway LoadBalancer 10.0.165.209 20.245.56.35 8080:30278/TCP 157m config-server ClusterIP 10.0.233.72 <none> 8888/TCP 163m customers-service ClusterIP 10.0.30.192 <none> 8080/TCP 171m discovery-server ClusterIP 10.0.184.95 <none> 8761/TCP 162m vets-service ClusterIP 10.0.94.74 <none> 8080/TCP 171m visits-service ClusterIP 10.0.84.138 <none> 8080/TCP 170mBoth the admin-server and the api-gateway should have an external IP.
You can also take a look in the MC resource group in the Azure portal. You will notice 2 Public IP addresses got created.
-
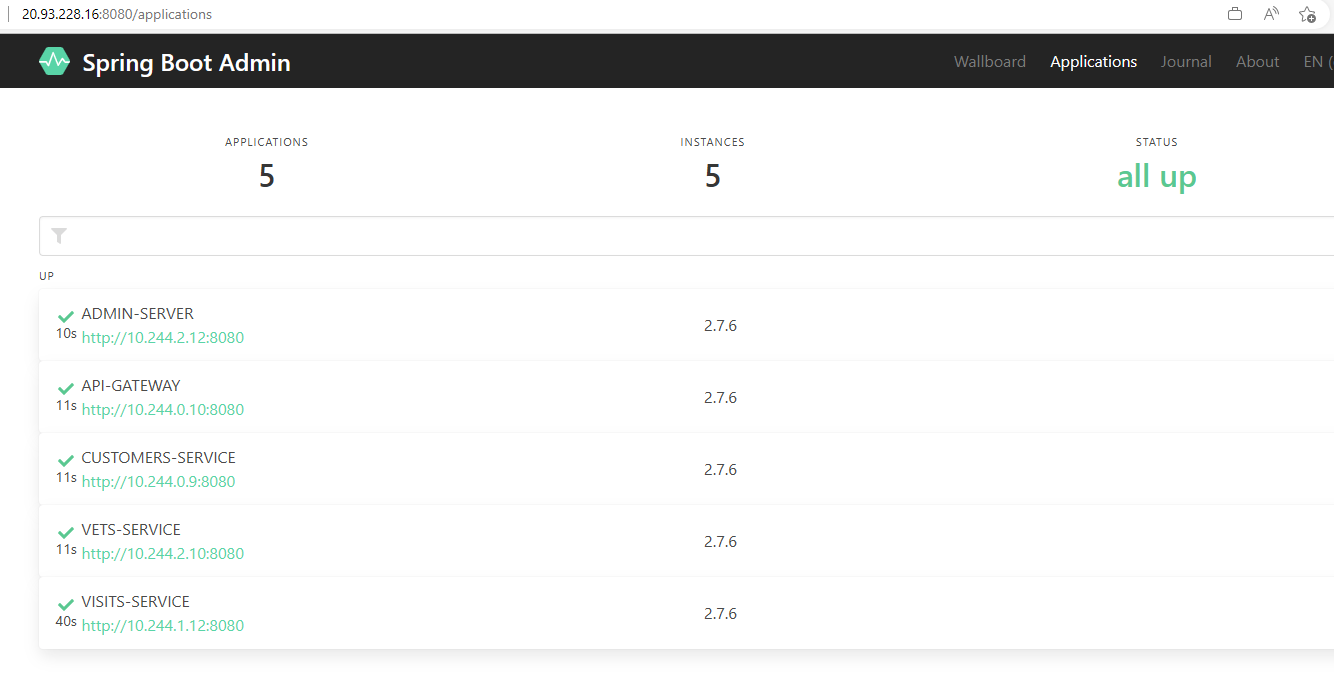
Copy the external IP of the admin-server and use a browser window to connect to port 8080. This will show you info about each of your applications.
-
Select Wallboard and next one of your microservices. The Admin server will show you internal info of your services.

-
Copy the external IP of the api-gateway and use a browser window to connect to port 8080. It should show you information on the pets and visits coming from your database.
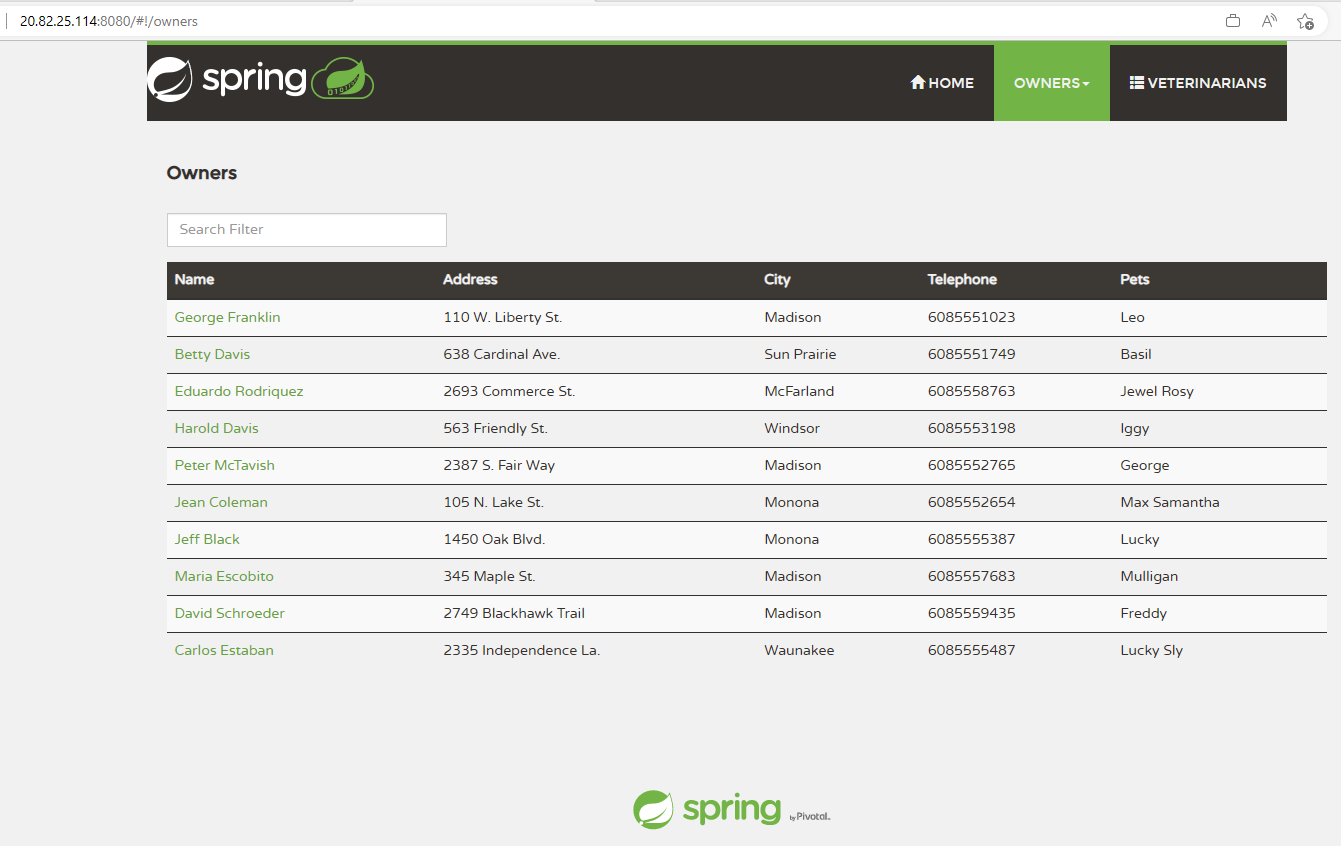
You now have the Spring Petclinic application running properly on the AKS cluster.
-
In case you are not seeing any data in your application, you can troubleshoot this issue by interactively connecting to your MySQL Flexible Server and querying your databases and tables.
az mysql flexible-server connect -n $MYSQL_SERVER_NAME -u myadmin -p $MYSQL_ADMIN_PASSWORD --interactive show databases; use petclinic; show tables; select * from owners;For the MySQL Flexible Server connection to work, you will need to have your local IP address added to the MySQL Flexible Server firewall.
Once you got everything up and running, you are now probably very eager to push your code changed to a GitHub repository. Be mindful though when you do this: Do not push your GitHub PAT token (it’s in the local
application.ymlfile of the config-server) to a remote repository. It will immediately invalidate the PAT token and your config-server will start failing. You should exclude theapplication.ymlfile from your commit. You can also check out the LabTips on how to recover from this in case you did accidentally push the PAT token to your remote repo.