Step 6: Run Functions Locally and Test with Cloud Resources¶
Now that local.settings.json points to your actual Azure resources provisioned by azd and the Durable Task emulator is running, we can start the Function App and perform end-to-end testing.
-
Authenticate with Azure:
For access to Azure resources, you'll need to perform an az login:
All platforms:
Follow the authentication prompts in your browser. After successful login, if you have multiple subscriptions, select the appropriate one from the terminal.
-
In the same terminal where you activated the virtual environment in Step 3, ensure you're in the src directory:
Your terminal prompt should still show (.venv) indicating the virtual environment is active.
-
Start the Azure Functions runtime locally (ensure your venv from Step 3 is still activated):
All platforms:
Note: This may take a minute to start.
-
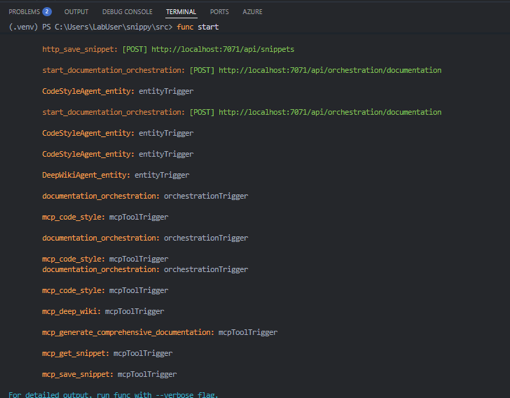
Look for output indicating the Functions host has started successfully. You should see your functions listed, including the HTTP endpoints, the MCP tool trigger functions, and even an orchestration (we'll run this soon), as shown below:
6.1 Test with REST Client (End-to-End Smoke Test) - Optional¶
Let's test your implementation using the built-in REST Client:
-
In VS Code Explorer, open src/tests/test.http. This file contains pre-defined HTTP requests for testing different Snippy endpoints.
-
Find the request block labeled ### Save a new snippet with projectId. Select the small "Send Request" link directly above the POST line.
-
Check the response panel that appears on the right. You should see a Status 200 OK response with JSON data showing the saved snippet details, confirming that:
- Your function successfully processed the request
- Azure OpenAI generated embeddings for the code
- The snippet was stored in Cosmos DB with its vector embedding
-
Now test retrieval: Find the ### Get a snippet by name request block. Modify the snippet name in the URL (/api/snippets/{name}) to match the one you just saved (the default is "test-snippet"). Send this request and verify it returns the correct code snippet data.
-
Test a few more operations to ensure everything works:
- Save a more complex snippet using the ### Save a complex snippet request
- Retrieve it using the corresponding GET request
- Try the AI agent functions by running the ### Generate wiki or ### Generate code style guide requests
-
For the agent-based functions (wiki and code style guide), note that these may take longer to execute (10-30 seconds) as they involve creating an AI agent that analyzes your saved snippets.
These successful tests confirm that your entire pipeline is working: HTTP endpoints, embedding generation, Cosmos DB vector storage, and AI agent integration.